Asphalt pavement is a critical component of modern infrastructure, serving as the backbone for roads, runways, parking lots, and other paved surfaces. Asphalt additives have become increasingly common, providing enhanced performance and longevity to these surfaces. Among these additives, gilsonite—a naturally occurring hydrocarbon resin—stands out for its remarkable properties.
The Benefits of Gilsonite in Asphalt Pavement are evident in its ability to improve durability, enhance resistance to rutting and cracking, and reduce maintenance costs. In this article, we will explore how these benefits translate into better performance and cost savings for asphalt pavements.
If you’re planning a road project, you can buy gilsonite for asphalt production and improve your results significantly.
Additionally, trusted experts at AsiaGilsonite have been instrumental in pioneering the use of this innovative resin, further solidifying its reputation in the industry.
What Are the Benefits of Gilsonite in Asphalt Pavement
Gilsonite, also known as uintaite or asphaltum, is a naturally occurring hydrocarbon resin that is mined from different resources worldwide. It has been used in asphalt pavement for many years and can provide several benefits, including:
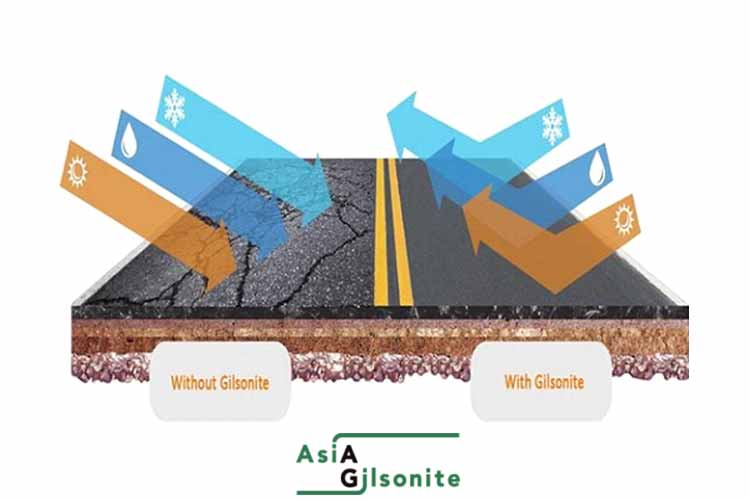
Improved Resistance to Aging
Uintaite can help improve the resistance of asphalt paving to aging caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation and other environmental factors. This can help prevent the pavement from getting cracked and becoming brittle over time.
Enhanced Flexibility
The use of asphaltum can improve the flexibility of asphalt pavement, allowing it to better withstand the stresses and strains caused by heavy traffic and temperature fluctuations. This can help prevent cracking and other forms of pavement failure.
Reduced Thermal Cracking
Uintaite can help reduce thermal cracking in the asphalt pavement by improving the binder’s resistance to temperature changes. This can help prevent the asphalt pavement from cracking due to expansion and contraction caused by temperature fluctuations.
Increased Skid Resistance
The increased skid resistance of pavement is another benefit of uintaite that improves safety for drivers and pedestrians by reducing the risk of skidding and slipping.
Environmentally Sustainable
Asphaltum is a naturally occurring substance that can be mined and used without the need for energy-intensive manufacturing processes. This makes it a more environmentally sustainable choice for paving asphalt compared to synthetic additives that may have a greater environmental impact.
Improved Adhesion
Gilsonite has a high affinity for asphalt binders, which can improve the adhesion between the binder and the aggregate in the pavement. This can help prevent stripping and other forms of asphalt pavement failure caused by poor adhesion.
Reduced Pavement Noise
Uintaite can help reduce pavement noise by increasing the stiffness of the pavement, which can reduce the vibration caused by traffic.
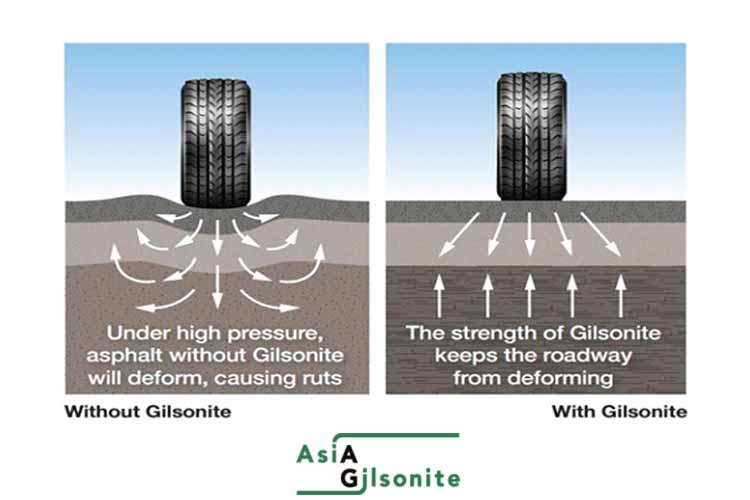
Enhanced Resistance to Deformation
Asphaltum improves the resistance of sulfonated asphalt pavement to deformation caused by heavy traffic or high temperatures. This can help prevent rutting, shoving, and other types of pavement deformation.
Increased Resistance to Moisture Damage
Uintaite has hydrophobic properties, which can help improve the resistance of asphalt to moisture damage caused by rain, snow, and other forms of precipitation.
Improved Workability
Uintaite can improve the workability of asphalt binder, making it easier to mix and apply during construction. This helps ensure consistent asphalt pavement quality and reduces construction time and costs.
Improved Durability
The improved durability and longevity of sulfonated asphalt pavement are one of the many benefits of asphaltum in asphalt. It has a high melting point and is resistant to oxidation and weathering, which can help prevent cracking and other forms of damage over time.
Increased Stiffness
Gilsonite can increase the stiffness of paving asphalt, which can help improve its resistance to deformation and rutting.
Enhanced Binder Performance
Uintaite improves the performance of asphalt binder by increasing its viscosity and reducing its susceptibility to low-temperature cracking.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
By improving the durability and longevity of asphalt pavement, the use of uintaite can help reduce maintenance costs over the life of the pavement.
Environmentally Friendly
Asphaltum is a natural product that is mined from the earth and does not contain any harmful chemicals or additives, making it an environmentally friendly choice for asphalt paving.
Improved Resistance to Chemical Degradation
Uintaite can help improve the resistance of asphalt paving to chemical degradation caused by exposure to fuels, oils, and other chemicals. This can help prevent the pavement from deteriorating prematurely and reduce the need for frequent repairs.
Increased Resistance to Fatigue Cracking
Gilsonite can help increase the resistance of asphalt paving to fatigue cracking caused by repeated loading and unloading cycles. This can help extend the life of the asphalt pavement and reduce maintenance costs.
Enhanced Color Stability
The asphalt paving color stability can simply be improved by adding uintaite to it and preventing it from fading or discoloring due to exposure to UV radiation and other environmental factors.
Improved Workability in Cold Weather
Workability, especially during construction time is of importance. Therefore, uintaite can help improve the workability of asphalt binder in cold weather, making it easier to mix and apply during construction. This can help reduce construction time and costs, as well as improve the quality of the pavement.
Reduced Aging of Asphalt Binder
Finally, uintaite can help reduce the aging of asphalt binders caused by exposure to oxygen and other environmental factors. This can help extend the life of the pavement and reduce maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Gilsonite is an effective and versatile additive for asphalt pavement, offering numerous benefits for infrastructure projects. The unique properties of Gilsonite, including its high melting point, superior bonding characteristics, and excellent resistance to rutting and cracking, make it an ideal choice for enhancing the durability and performance of asphalt paving. By incorporating uintaite into pavement materials, engineers and contractors can improve the longevity of their projects, reduce maintenance costs, and minimize the environmental impact of asphalt production. As such, asphaltum represents a valuable investment in the future of infrastructure projects, ensuring safe and reliable transportation for communities around the world.